Sensory Pathways
Spinal Cord and Brain Stem
A sensory pathway that carries peripheral sensations to the brain is referred to as an ascending pathway, or ascending tract. The various sensory modalities each follow specific pathways through the CNS. Tactile and other somatosensory stimuli activate receptors in the skin, muscles, tendons, and joints throughout the entire body. However, the somatosensory pathways are divided into two separate systems on the basis of the location of the receptor neurons. Somatosensory stimuli from below the neck pass along the sensory pathways of the spinal cord, whereas somatosensory stimuli from the head and neck travel through the cranial nerves—specifically, the trigeminal system.
The dorsal column system (sometimes referred to as the dorsal (or posterior) column-medial lemniscus) and the spinothalamic tract are two major pathways that bring sensory information to the brain (Figure). The sensory pathways in each of these systems are composed of three successive neurons.
The dorsal column system begins with the axon of a dorsal root ganglion neuron entering the dorsal root and joining the dorsal column white matter in the spinal cord. As axons of this pathway enter the dorsal column, they take on a positional arrangement so that axons from lower levels of the body position themselves medially, whereas axons from upper levels of the body position themselves laterally. The dorsal column is separated into two component tracts, the fasciculus gracilis that contains axons from the legs and lower body, and the fasciculus cuneatus that contains axons from the upper body and arms.
The axons in the dorsal column terminate in the nuclei of the medulla, where each synapses with the second neuron in their respective pathway. The nucleus gracilis is the target of fibers in the fasciculus gracilis, whereas the nucleus cuneatus is the target of fibers in the fasciculus cuneatus. The second neuron in the system projects from one of the two nuclei and then decussates, or crosses the midline of the medulla. These axons then continue to ascend the brain stem as a bundle called the medial lemniscus. These axons terminate in the thalamus, where each synapses with the third neuron in their respective pathway. The third neuron in the system projects its axons to the postcentral gyrus of the cerebral cortex, where somatosensory stimuli are initially processed and the conscious perception of the stimulus occurs.
The spinothalamic tract also begins with neurons in a dorsal root ganglion. These neurons extend their axons to the dorsal horn, where they synapse with the second neuron in their respective pathway. The name "spinothalamic" comes from this second neuron, which has its cell body in the spinal cord gray matter and connects to the thalamus. Axons from these second neurons then decussate within the spinal cord and ascend to the brain and enter the thalamus, where each synapses with the third neuron in its respective pathway. The neurons in the thalamus then project their axons to the spinothalamic tract, which synapses in the postcentral gyrus of the cerebral cortex.
These two systems are similar in that they both begin with dorsal root ganglion cells, as with most general sensory information. The dorsal column system is primarily responsible for touch sensations and proprioception, whereas the spinothalamic tract pathway is primarily responsible for pain and temperature sensations. Another similarity is that the second neurons in both of these pathways are contralateral, because they project across the midline to the other side of the brain or spinal cord. In the dorsal column system, this decussation takes place in the brain stem; in the spinothalamic pathway, it takes place in the spinal cord at the same spinal cord level at which the information entered. The third neurons in the two pathways are essentially the same. In both, the second neuron synapses in the thalamus, and the thalamic neuron projects to the somatosensory cortex.
Ascending Sensory Pathways of the Spinal Cord
The left panel shows the dorsal column system and its connection to the brain. The right column shows the spinothalamic tract and its connection to the brain.
The dorsal column system and spinothalamic tract are the major ascending pathways that connect the periphery with the brain.
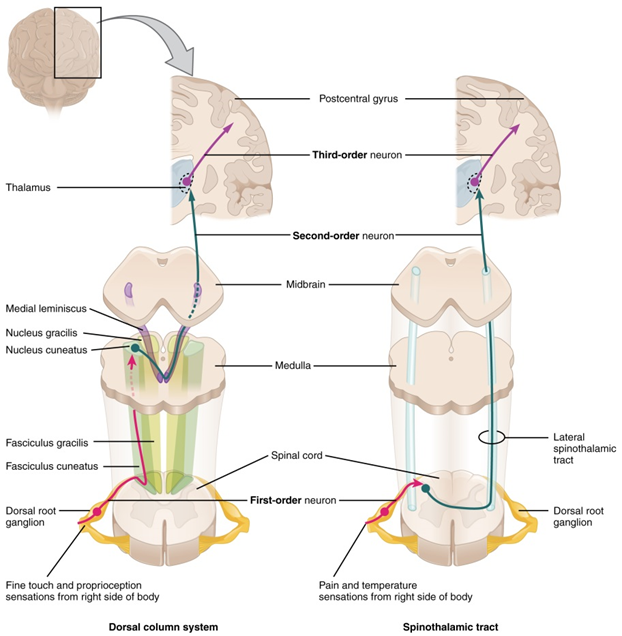
Figure 9. The dorsal column system and spinothalamic tract (both seen here with blue arrows) are the major ascending pathways that connect the periphery with the brain.
Appendicular Control
The lateral corticospinal tract is composed of the fibers that cross the midline at the pyramidal decussation (see Figure). The axons cross over from the anterior position of the pyramids in the medulla to the lateral column of the spinal cord. These axons are responsible for controlling appendicular muscles.
This influence over the appendicular muscles means that the lateral corticospinal tract is responsible for moving the muscles of the arms and legs. The ventral horn in both the lower cervical spinal cord and the lumbar spinal cord both have wider ventral horns, representing the greater number of muscles controlled by these motor neurons. The cervical enlargement is particularly large because there is greater control over the fine musculature of the upper limbs, particularly of the fingers. The lumbar enlargement is not as significant in appearance because there is less fine motor control of the lower limbs.
Axial Control
The anterior corticospinal tract is responsible for controlling the muscles of the body trunk (see Figure). These axons do not decussate in the medulla. Instead, they remain in an anterior position as they descend the brain stem and enter the spinal cord. These axons then travel to the spinal cord level at which they synapse with a lower motor neuron. Upon reaching the appropriate level, the axons decussate, entering the ventral horn on the opposite side of the spinal cord from which they entered. In the ventral horn, these axons synapse with their corresponding lower motor neurons. The lower motor neurons are located in the medial regions of the ventral horn, because they control the axial muscles of the trunk.
Because movements of the body trunk involve both sides of the body, the anterior corticospinal tract is not entirely contralateral. Some collateral branches of the tract will project into the ipsilateral ventral horn to control synergistic muscles on that side of the body, or to inhibit antagonistic muscles through interneurons within the ventral horn. Through the influence of both sides of the body, the anterior corticospinal tract can coordinate postural muscles in broad movements of the body. These coordinating axons in the anterior corticospinal tract are often considered bilateral, as they are both ipsilateral and contralateral.
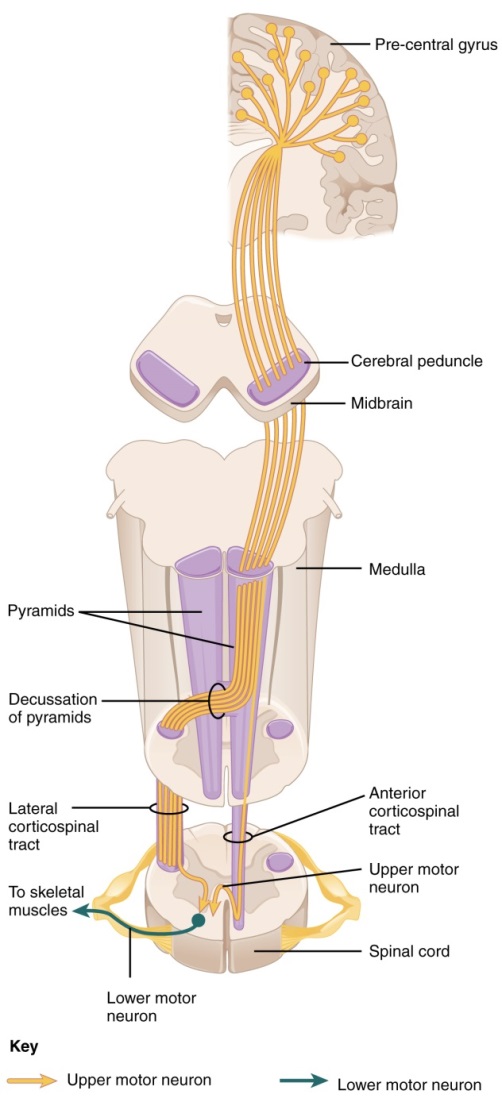
Figure 10. The major descending tract that controls skeletal muscle movements is the corticospinal tract. It is composed of two neurons, the upper motor neuron (yellow arrows) and the lower motor neuron (green arrow). The upper motor neuron has its cell body in the primary motor cortex of the frontal lobe, crosses over (or decussates) in the pyramids of the medulla, and synapses on the lower motor neuron, which is in the ventral horn of the spinal cord and projects to the skeletal muscle in the periphery.