Functional and Anatomical Organization
Your nervous system is similar to the speaker analogy. Your nervous system has two major divisions, the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS is composed of the brain and the spinal cord. This division receives sensory input, integrates it, and sends out the appropriate motor output. The peripheral nervous system makes up the rest of the nervous system. The peripheral nervous system contains nerves that conduct information into and out of the CNS. The PNS itself has two major divisions, the sensory division and the motor division. The sensory division senses both the internal environment and the external environment. It is sometimes called the afferent division because it conducts information into the CNS. The motor division is the efferent division because it conducts information out of the CNS to effectors such as muscles and glands.
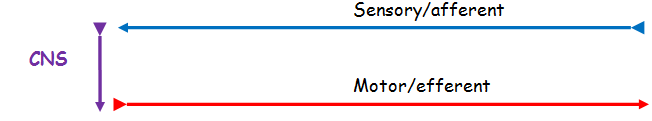
Figure 1. Sensory or afferent neurons (represented here by a blue arrow) take sensory information to the CNS (represented here by a purple downwardarrow) while Motor or efferent neurons (represented here by a red arrow) send signals from the CNS to the muscles and glands.
The motor division has two subdivisions, the somatic division and the autonomic division. The somatic division is the part that you can consciously control. The autonomic division controls smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands. The autonomic nervous system has two divisions, the sympathetic division and the parasympathetic division. The sympathetic division prepares your body for stress. It would be the division involved if you came face to face with an angry bear. The parasympathetic division is the division involved with times of low stress - imagine being kicked back on the beach in a nice comfy chair at sun set with no aggravations at all.

Figure 2. The Divisions of the Nervous System. The Central Nervous System receives information from the Peripheral Nervous System's Sensory division and sends output through the Motor division of the PNS. The Motor division includes the Autonomic and Somatic divisions. The ANS includes the Sympathetic and Parasympathetic divisions.
In our stereo analogy, the amplifier would represent the CNS because it receives input signals and produces output signals. The stereo components that send sound into the amplifier would represent sensory organs and their input (afferent) wires, which go into the amplifier, would represent sensory nerves. The speakers would be the effectors because they are what the amplifier controls. The wires going out of the speakers (efferent) would represent the motor nerves. Of course in a stereo system, there are all sorts of different types of wires, cables, and connectors that are used to hook the components together. Inside each component, there is a staggering array of other wires, circuit boards and who knows what all else. Again, nervous systems are not composed of wires, but there are different types of cells.

