Gross and Microscopic Anatomy of Nerve Tissue - Neuron Anatomy and Physiology
Objectives
By the end of the section the student will be able to:
- Describe the basic structure of a neuron
- Describe the functions of each part of the neuron
The cell involved with transmitting information in the nervous system is called a "neuron." There are three kinds of neurons functionally speaking. These are the sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons. Sensory neurons are afferent neurons that conduct information into the CNS. Motor neurons are efferent neurons that conduct information out of the CNS. The interneurons are housed entirely within the CNS and are the ones responsible for integration of information.
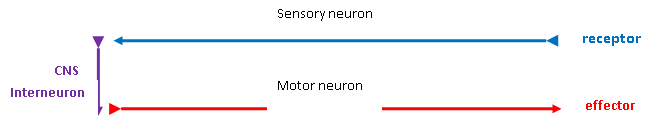
Figure 1. Functions of the Nervous System. Sensory input from a receptor (monitors internal and external stimuli from the skin or organs) sends an impulse signal to the Central Nervous System and an Interneuron there where the brain and spinal cord will process sensory input and send out a response. The motor output will send a signal to control muscles and glands, which are the effectors.


