Eukaryotic Cells
Now, let us break down the word Eukaryote. The prefix of "eu" means true. We have already learned the definition of "kary" is the nucleus. We can determine that eukaryotes do have a nucleus with this information.
Eukaryotes are typical organisms that include fungi, plants, and animals and are typically larger than prokaryotes. They also contain a nucleus with a double membrane. Eukaryotic cells contain highly structured cytoplasmic structures called organelles and contain one to several thousand mitochondria. These cells are usually multicellular organisms with specialized cells.
Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have:
- Membrane-bound nucleus
- Numerous membrane-bound organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, chloroplasts, mitochondria, and others
- Several rod-shaped chromosomes
Because a membrane surrounds a eukaryotic cell's nucleus, it is often said to have a "true nucleus". The word "organelle" means "little organ", and, as already mentioned, organelles have specialized cellular functions, just as the organs of your body have specialized functions. Organelles allow different functions to be compartmentalized in different areas of the cell.
| Cell Parts | Structure | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Genetic Control | ||
| Nucleus |  |
DNA synthesis, RNA synthesis; assembly of ribosomal subunits (in nucleolus) |
| Ribosomes |  |
A sphere-shaped structure within the cytoplasm of a cell that is composed of RNA and protein and is the site of protein synthesis. |
| Manufacturing, Distribution, and Breakdown | ||
| Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum | 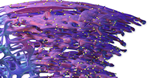 |
Synthesis of membrane lipids and proteins, secretory proteins and hydrolic enzymes; formation of transport vesicles |
| Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum | 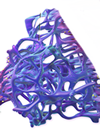 |
Synthesis of lipids; detoxification in liver cells; calcium ion storage |
| Golgi Apparatus |  |
Modification and sorting of macromolecules formation of lysosomes and transport vesicles |
| Lysosomes | Digestion (food vacuole); storage pf chemicals and cell enlargement (central vacuole); water balance (contractile vacuole) | |
| Peroxisomes |  |
Diverse metabolic processes, with breakdown of toxic hydrogen peroxide by-product |
| Vacuoles |  |
Contain substances that recently entered the cell, store and transport new molecules |
| Energy Processing | ||
| Mitochondria | Conversion of chemical energy in food to chemical energy of ATP | |
| Structural Support, Movement, and Communication Between Cells | ||
| Cytoskeleton (micro-filaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules | 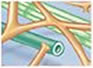 |
Maintenance of cell shape, anchorage of organelles; movement of organelles within cells; cell movement; bending of cilia and flagella |
| Cell Junctions | 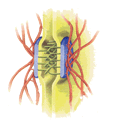 |
Communication between cells; binding of cells in tissues |
|
Extracellular Matrix |
 |
Binding of cells in tissues; surface protection, regulation of cellular activities |



