Monosaccharides, Disaccharide, and Polysaccharides
Monosaccharides (mono- = "one"; sacchar- = "sweet") are simple sugars, the most common of which is glucose. In monosaccharides, the number of carbons usually ranges from three to seven. Most monosaccharide names end with the suffix -ose.
Disaccharides (di- = "two") form when two monosaccharides undergo a dehydration reaction (also known as a condensation reaction or dehydration synthesis). During this process, the hydroxyl group of one monosaccharide combines with the hydrogen of another monosaccharide, releasing a molecule of water and forming a covalent bond.
Polysaccharides are a long chain of monosaccharides linked by glycosidic bonds known as a polysaccharide (poly = "many"). The chain may be branched or unbranched, and it may contain different types of monosaccharides.
| Monosaccharides | Disaccharides (monomers) | Polysaccharides (monomers) |
|---|---|---|
| Glucose | Sucrose (glucose and fructose) | Starch (glucose) |
| Fructose | Lactose (galactose and glucose) | Glycogen (glucose) |
| Ribose | Maltose (glucose) | Cellulose (glucose) |
| Glyceraldehyde | Chitin (glucose) | |
| Galactose | ||
| Ribulose | ||
| Dihydroxyacetone (also known as DHA and glycerone) |
Plants and animals store energy in the form of polysaccharides. These storage molecules are chains of glucose monomers arranged in different ways, each functioning differently. Plants store energy in the form of the polysaccharide, also known as starch. Starch consists of single long chains of glucose monomers linked together via the dehydration reaction.

Figure 1. Displays the chemical formula of a starch molecule, (C6H10O5)n.
CC BY: Tiffany Blacburn
Glycogen is the storage form of glucose in humans and other vertebrates and is made up of monomers of glucose. Glycogen is the animal equivalent of starch and is a highly branched molecule usually stored in liver and muscle cells. Whenever blood glucose levels decrease, glycogen is broken down to release glucose in a process known as glycogenolysis.
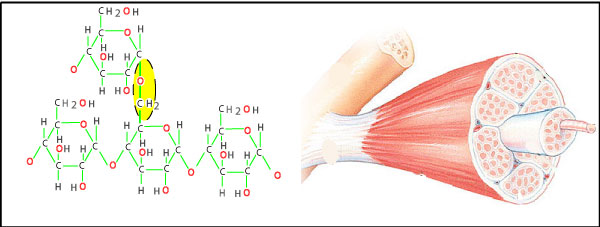
Figure 3. Animals store glucose for energy in the form of glycogen that consists of highly branched chains of glucose monomers. The formula for glycogen is (C6H10O5)n
CC BY: Tiffany Blackburn



