Microscopic Level of the Retina
Understand that the photoreceptors in the retina (rods and cones) are located behind the axons, RGCs, bipolar cells, and retinal blood vessels. A significant amount of light is absorbed by these structures before the light reaches the photoreceptor cells. However, at the exact center of the retina is a small area known as the macula, which has the central fovea. At the fovea, the retina lacks the supporting cells and blood vessels, and only contains photoreceptors. Therefore, visual acuity, or the sharpness of vision, is greatest at the fovea. This is because the fovea is where the least amount of incoming light is absorbed by other retinal structures (see Figure 4). As one moves in either direction from this central point of the retina, visual acuity drops significantly. In addition, each photoreceptor cell of the fovea is connected to a single RGC. Therefore, this RGC does not have to integrate inputs from multiple photoreceptors, which reduces the accuracy of visual transduction. Toward the edges of the retina, several photoreceptors converge on RGCs (through the bipolar cells) up to a ratio of 50 to 1. The difference in visual acuity between the fovea and peripheral retina is easily evidenced by looking directly at a word in the middle of this paragraph. The visual stimulus in the middle of the field of view falls on the fovea and is in the sharpest focus. Without moving your eyes off that word, notice that words at the beginning or end of the paragraph are not in focus. The images in your peripheral vision are focused by the peripheral retina, and have vague, blurry edges and words that are not as clearly identified. As a result, a large part of the neural function of the eyes is concerned with moving the eyes and head so that important visual stimuli are centered on the fovea.
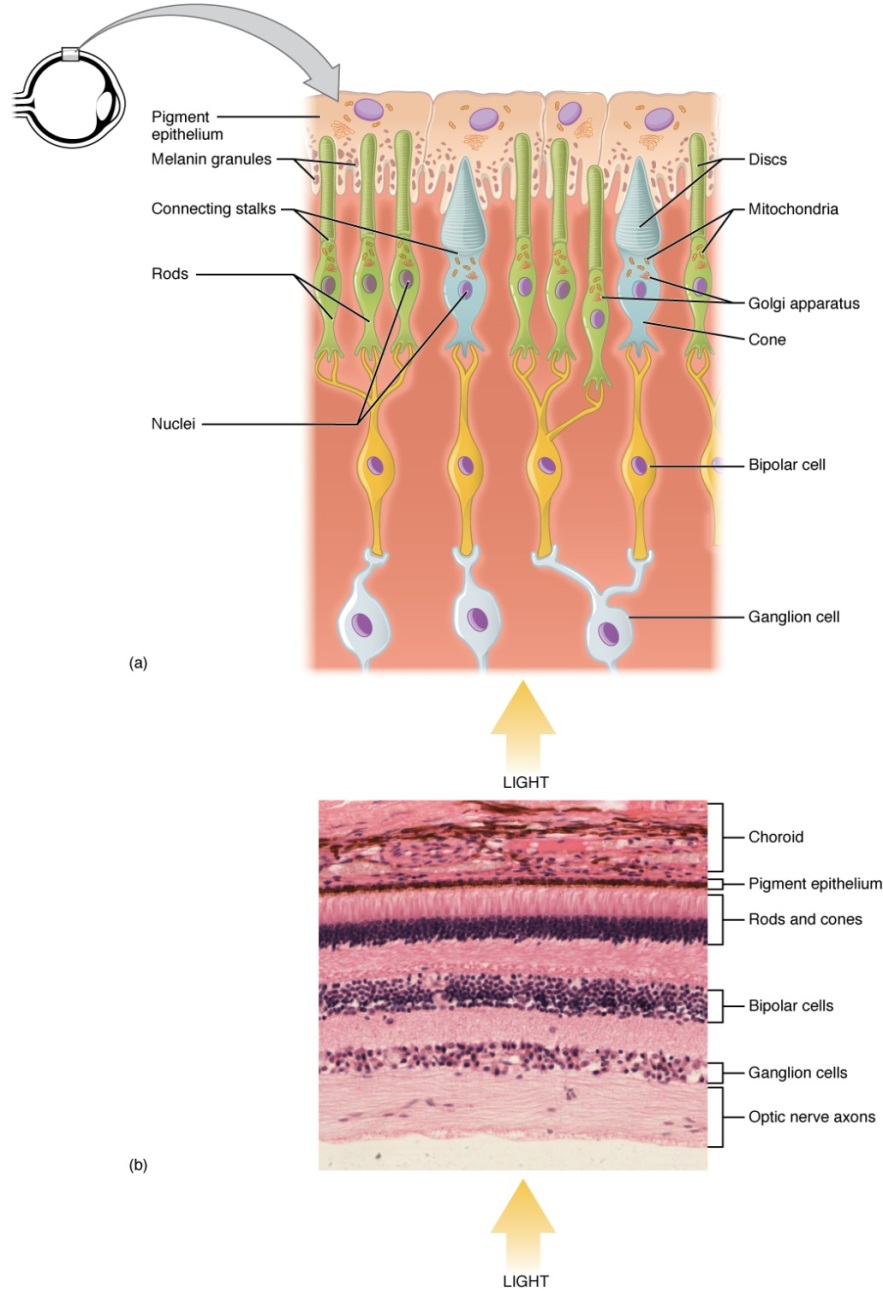
Figure 4. The Retina showing the direction that light passes on the retina. Notice that light passes through several layers of cells before reaching the rods and cones in the back of the eye. The cells that light passes through include ganglion cells, bipolar cells, rods and cones before it reaches the pigment epithelium. Notice also that the disc of the photoreceptors determines its name. The rods for example have rod shaped discs, while the cones have a disc that looks like an upside down cone.
