Meiosis I
Prophase I
During prophase I, the walls of the nucleus begin to break down, homologous chromosomes join together, and, chromosomes crossover and exchange segments. Homologous chromosomes exchange segments during crossing over, which increases the genetic variability in a population. After crossing over occurs, hollow structural tubes, called spindles, spread toward each pole of the cell. These spindles are held in place at the poles of the cell by centrioles, or barrel-shaped rings.

Figure 3. During this phase the nuclear walls begin to break down, homologous chromosomes come together, and chromosomes cross over or exchange genetic material. This is represented by the large blue X lining up with the large red X, and their exchanged genetic material is seen by the mismatched colored tips on each. The same is shown in the smaller blue x and red x, the come together and exchange a small portion of genetic material. After crossing over, spindles form toward each pole shown in a golden yellow and are held in place by the glowing yellow barrel-shaped centrioles.
Metaphase I
Next in the process, comes metaphase I. During this phase homologous pairs line up at the center line of the cell. The spindles, which are now completely spread across the cell, bind to each chromosome at its kinetochore.
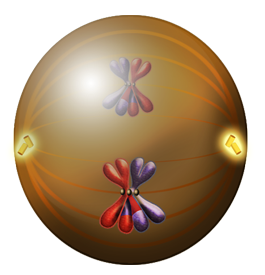
Figure 4. During this phase the homologous chromosomes (large red X and large blue X; small red x and small blue x) line up in the center of the cell and the spindles attach to each at the kinetochore (small grey circle at the center of each X).
Anaphase I
During the next stage, anaphase I, the spindles pull one homologue from each pair to opposite poles or sides of the cell.
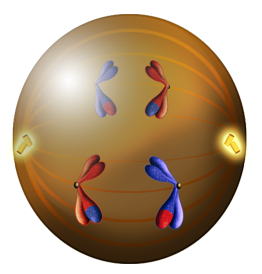
Figure 5. During this phase the spindles pull the homologous chromosomes apart (large blue X and small red x are pulled to the right while the large red X and small blue x are pulled to the left).
Telophase I
In the final phase of meiosis I, telophase I, a nuclear membrane forms around each set of sister chromatids, marking the completion of the first nuclear division. Consequently, the two new cells undergo cytokinesis, a process by which the cytoplasm is divided between the daughter cells.
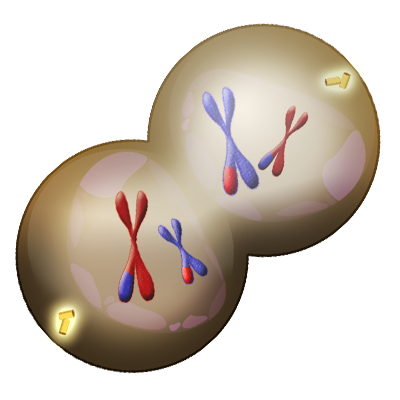
Figure 6. During the final phase of meiosis I, the nuclear membrane begins to reform (shown by the pale whitish circle surrounding each set of chromatids and the cells undergo cytokinesis and cleave the cytoplasm into two new daughter cells.
Meiosis Self-assessment
Match the following Meiosis l phases to the events of each phase.




