Meiosis II
Almost immediately after cytokinesis in meiosis I, meiosis II commences. In meiosis II, sister chromatids are separated. This division is very similar to a mitotic division and occurs in the same steps as both mitosis and meiosis I.
The key difference between meiosis II and a mitotic division is that crossing over does not occur during meiosis II. When the second meiotic division is completed, four non-identical haploid cells have been produced.
Prophase II
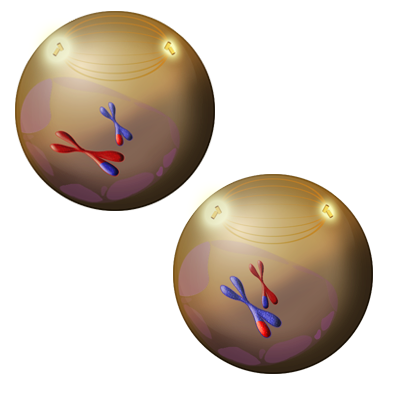
Figure 7. During the first phase of meiosis II, known as Prophase II the nuclear envelope breaks down (shown as a dissipating pale purple circle around the chromatids), and the golden yellow spindles form anchoring themselves at the glowing yellow barrel-shaped centriole.
Metaphase II
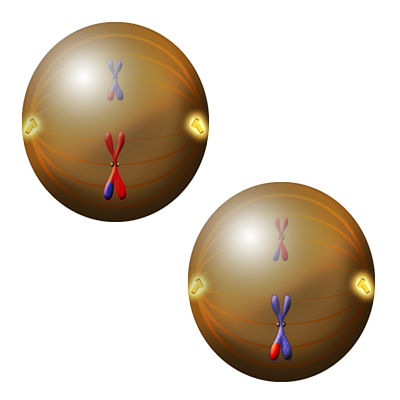
Figure 8. During Metaphase II, the sister chromatids line up across the middle of the cell, and the orange colored spindles attach at the kinetochores (small grey circle at the center of the X).
Anaphase II
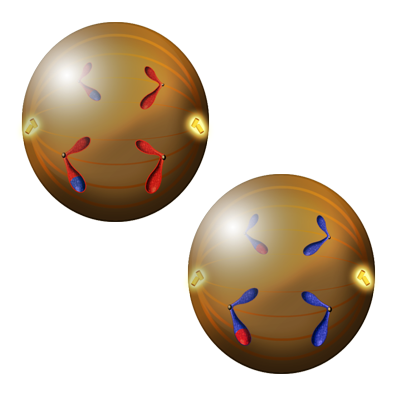
Figure 9. During Anaphase II, the sister chromatids are pulled apart in both cells (looks like each X is being split in half). In the first cell, the small red with a blue tip and large red with a blue tip are pulled to the left while the small red and large red are pulled to the right. In the second cell, the small blue with a red tip and large blue with a red tip are pulled to the left while the small blue and large blue are pulled to the right.
Telophase II
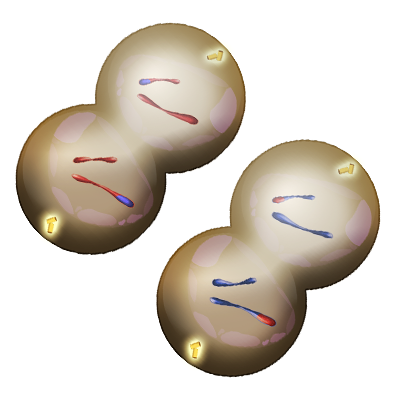
Figure 10. In the final stage of meiosis II, known as Telophase II, the nuclear membrane reforms (shown by the pale whitish circle) around each set of genetic material. The cells then undergo cytokinesis, forming four daughter cells in total.


