What is Loose Connective Tissue? Where is it Found? How Do We Recognize It?
Loose connective tissue binds organs together, it is found between different layers of tissues and between organs. For example, under the skin, and between muscles. It is made up of collagenous and elastic fibers suspended in a thick, ground substance with fibroblasts scattered throughout.
The following video discusses loose connective tissue.
![]()
![]()
Video 10. View the Connective Tissues video on YouTube (opens in a new window)
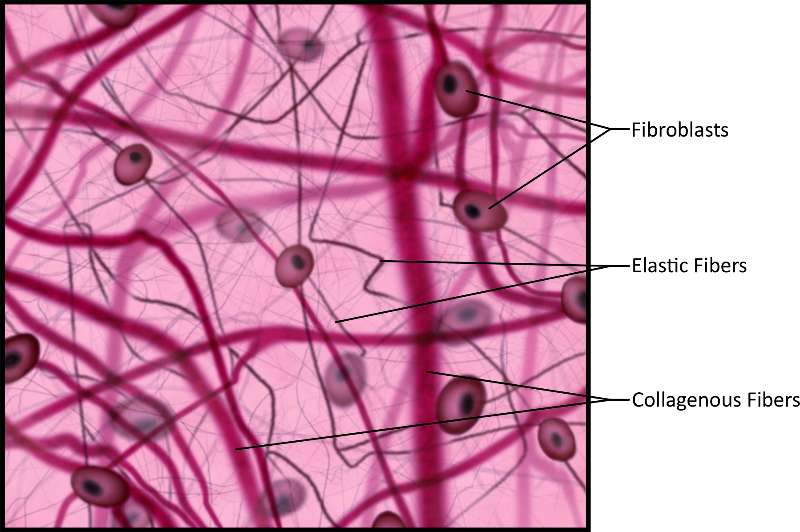
Figure 13. Illustration of connective tissue, often intersected by lines of various widths, representing elastic and collagenous fibers, which are produced in the simple oval-shaped fibroblasts also pictured.
What is the Purpose of Adipose Tissue and Where is it Found?
Adipose tissue provides protection, insulation and fat storage in large cells where the nucleus is pushed to the side by large areas for fat storage. It's found under the skin, behind the eyes, surrounding the heart and kidneys.
The following video discuses adipose tissue.
![]()
![]()
Video 11. View the Adipose Tissue video on YouTube (opens in a new window)
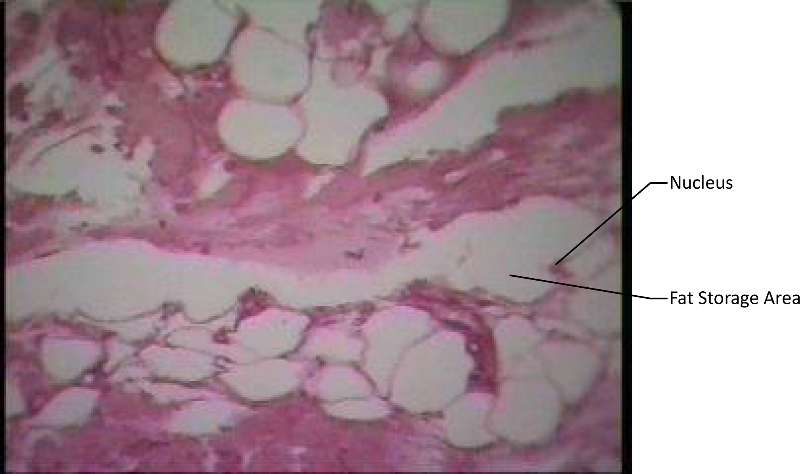
Figure 14. A micrograph dyed purple for ease of visabilty.
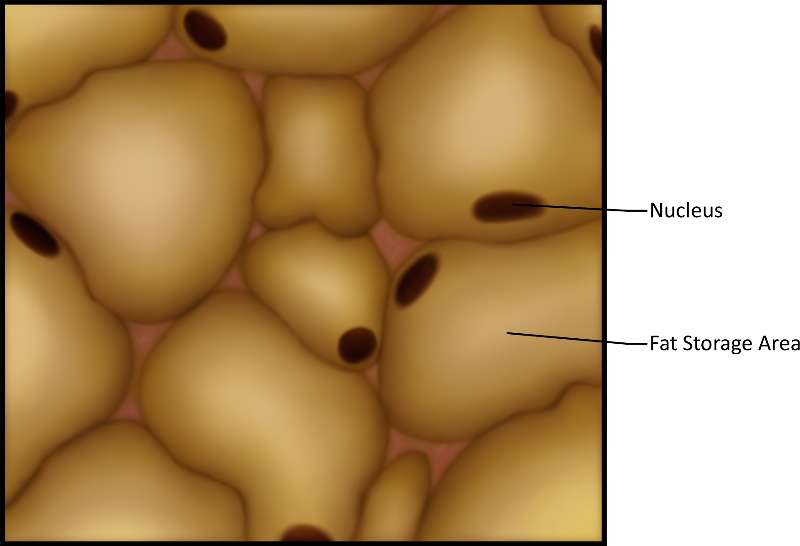
Figure 15. A close-up illustration; note the globular shape of the fat cells.
What is the Purpose of Hyaline Cartilage?
Hyaline cartilage is located in places such as at the ends of long bones, the end of the nose and in the trachea. It is made up of chondrocytes located in lacuna (which means chamber) in a matrix of chondrin. It's purpose is to provide protection and support.
The following video discusses hyaline cartilage.
![]()
![]()
Video 12. View the Hyaline Carilage video on YouTube (opens in a new window)
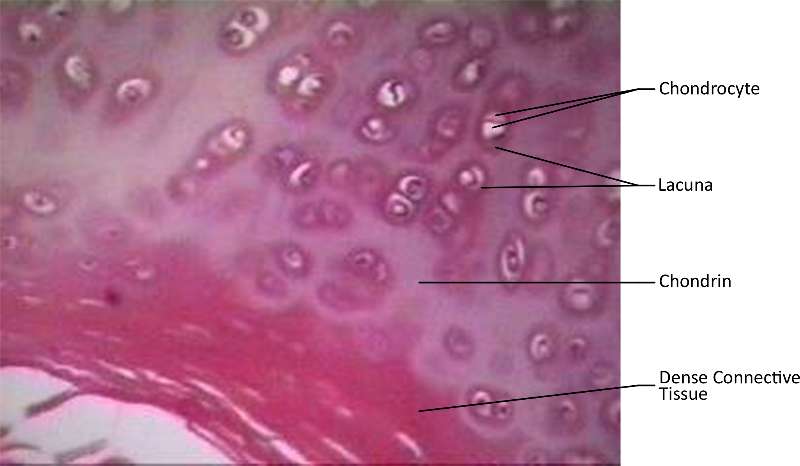
Figure 16. A cross-sections of hyaline cartilage in the trachea where the actual micrograph has been dyed purple for ease of visabilty.
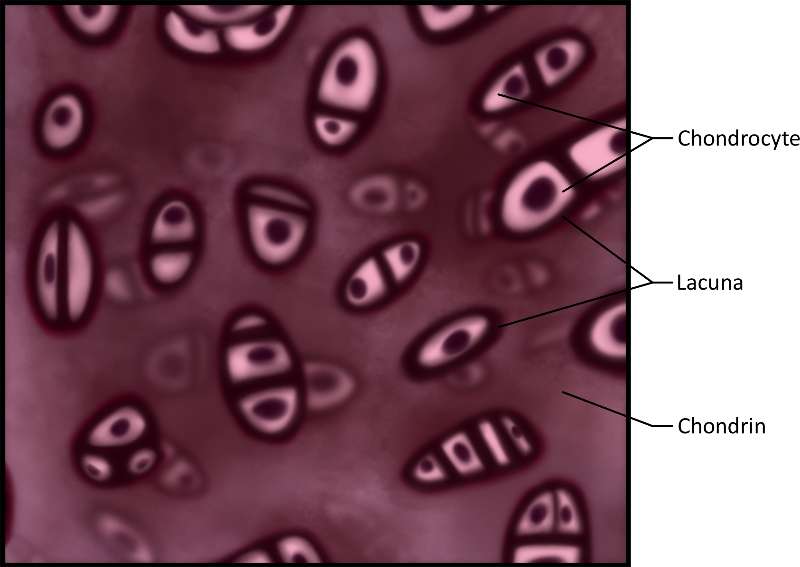
Figure 17. An illustration of hyaline cartilage in the trachea where the actual micrograph has been dyed purple for ease of visabilty.
What is Blood?
Blood is a connective tissue found in the blood vessels that is used for transport of nutrients, wastes, gases and hormones. . It is made up of red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets and fibrinogen in a matrix of liquid plasma.
The following video discusses blood.
![]()
![]()
Video 13. View the Blood video on YouTube (opens in a new window)
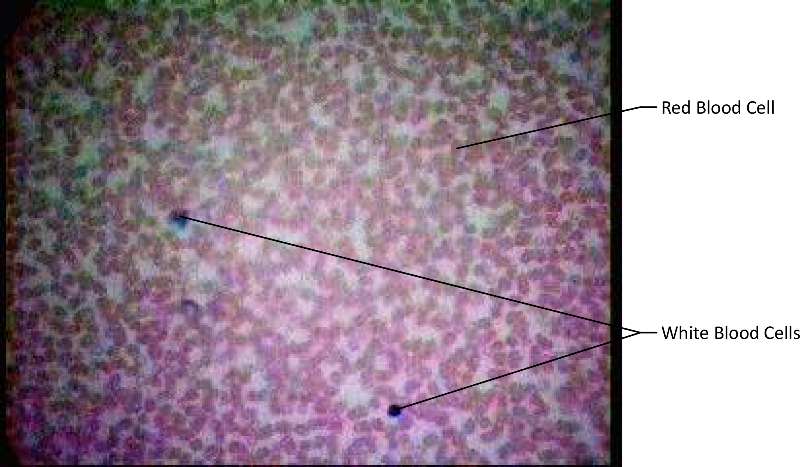
Figure 18. This image shows blood; note the larger size and complexity of white blood cells versus the smaller red disk-shaped red blood cells and is an actual micrograph.
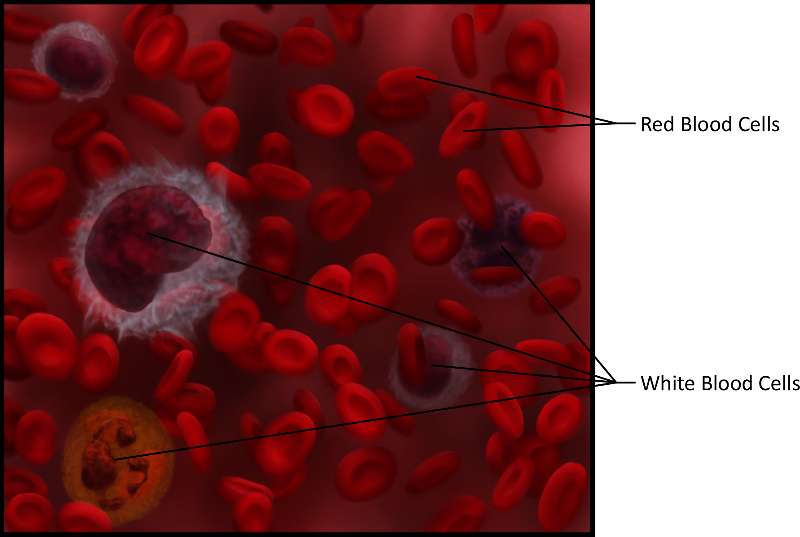
Figure 19. An illustration that shows blood. Notice the larger size and complexity of white blood cells versus the smaller red disk-shaped red blood cells and think about how this relates to their function.
What is the Purpose of Bone? What Does it Look Like?
Bone is a connective tissue where osteocytes are located in lacuna in a matrix of calcium salts. Bone functions for support and protection.
The following video discusses bone.
Video 14. View the Bone video on YouTube (opens in a new window)
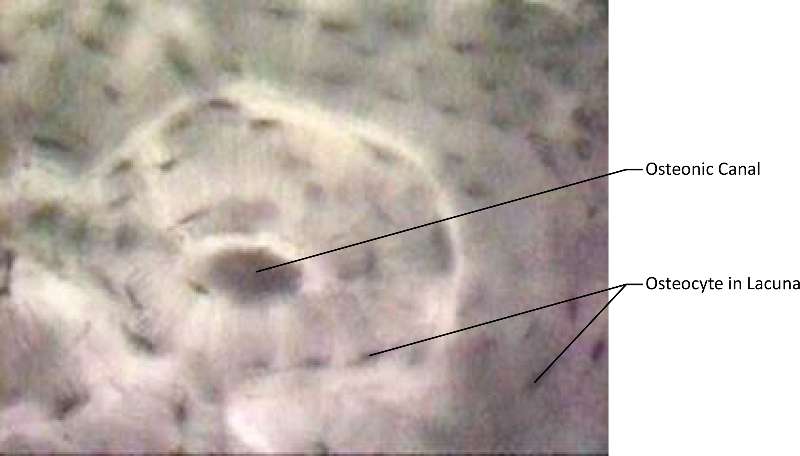
Figure 20. An actual micrograph of bone and that highlights the osteonic canal (which contains the bones blood supplies) and osteocyte(s) in lacuna.
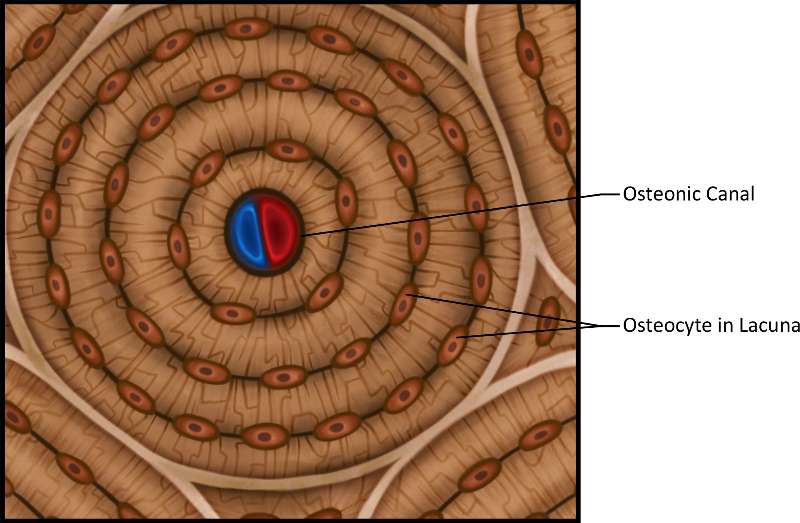
Figure 21. An illustration of bone and highlight the osteonic canal (which contains the bones blood supplies) and osteocyte(s) in lacuna.
Self-Check
| Drag the labels from the bottom to the correct slots. | ||



