What is Muscle Tissue? What Different Types are There and Where are They Found? What Do Different Types of Muscle Look Like?
Vertebrates have three types of muscle tissue; skeletal, cardiac and smooth. Muscle tissue has the ability to contract or to shorten and thicken to do work. This ability comes from the proteins found inside the muscle cells. The proteins may be arranged so that the cells look striped or striated with alternating light and dark bands. This is the situation with cardiac muscle and skeletal muscle, they are both striated. Smooth muscle is nonstriated because the proteins are arranged differently. Muscle tissue is controlled by the nervous system. Skeletal muscle is controlled by the somatic nervous system which means it is voluntary and under your conscious control. Smooth and cardiac muscle is controlled by the autonomic nervous system which means it is involuntary and you cannot consciously control it.
| Tissue | Structure | Function | Representative Location |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Skeletal Muscle |
polynuclear, long, striated cells |
Move bones |
attached to bones |
|
Smooth Muscle |
small tapered cells with one nucleus centrally located, nonstriated |
peristalsis, constriction of lumen |
walls of hollow organs |
|
Cardiac Muscle |
Uninuclear, striated, branched cells with intercalated disks |
contraction of heart, move blood |
heart |
The following video discusses muscle tissue.
![]()
![]()
Video 15. View the Muscle Tissue video on YouTube (opens in a new window)
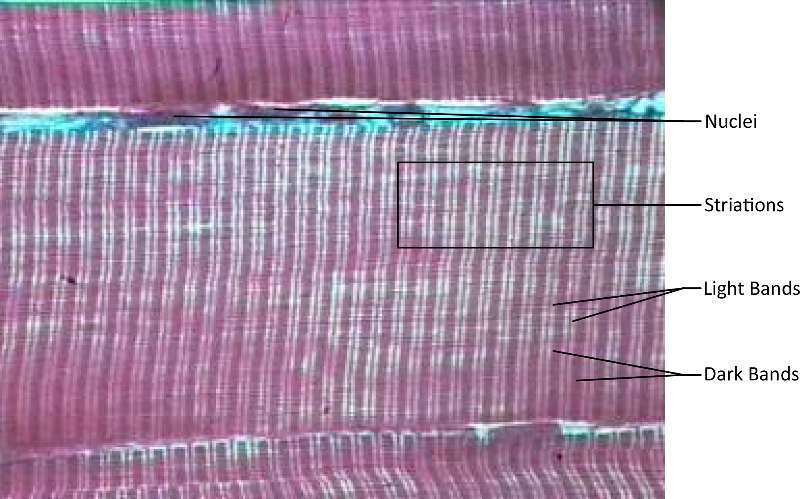
Figure 22. A micrograph of skeletal muscle composed of cell nuclei, striations, light bands and dark bands (dyed purple for ease of visibility).
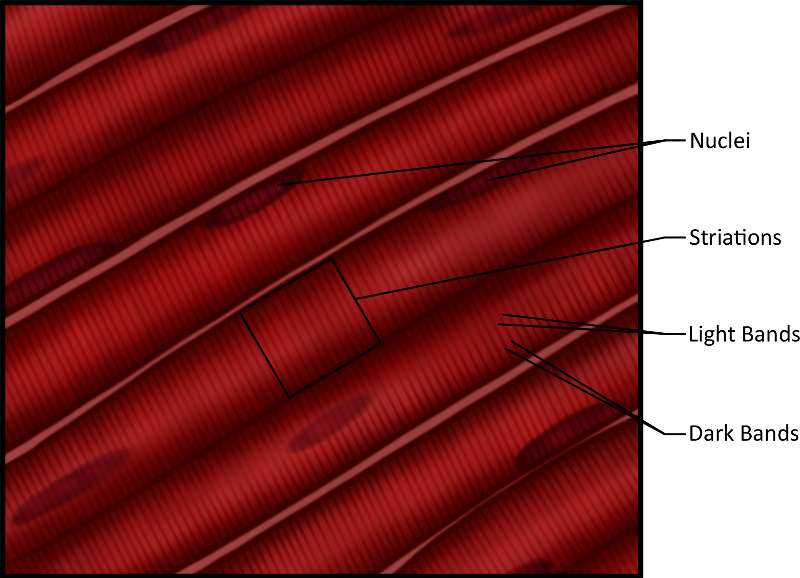
Figure 23. An illustration showing skeletal muscle composed of cell nuclei, striations, light bands and dark bands.
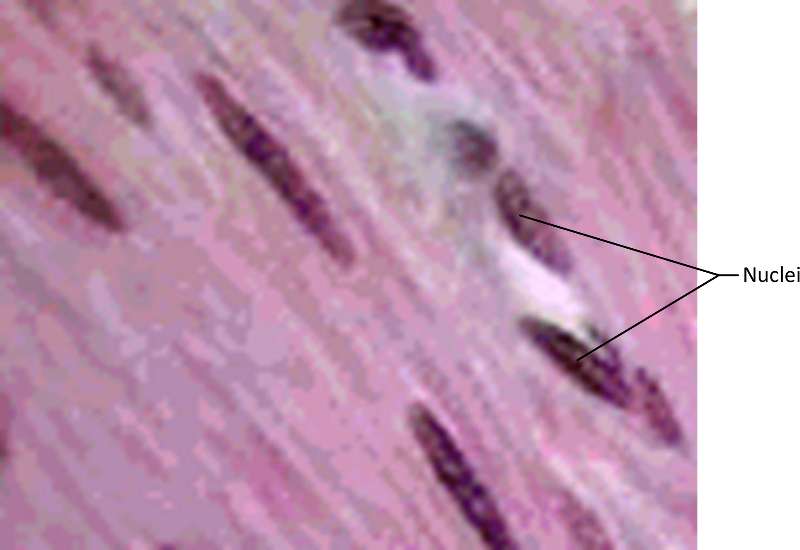
Figure 24. A micrograph showing smooth muscle dyed purple for ease of visibilty The darkest stained cells are the nuclei.
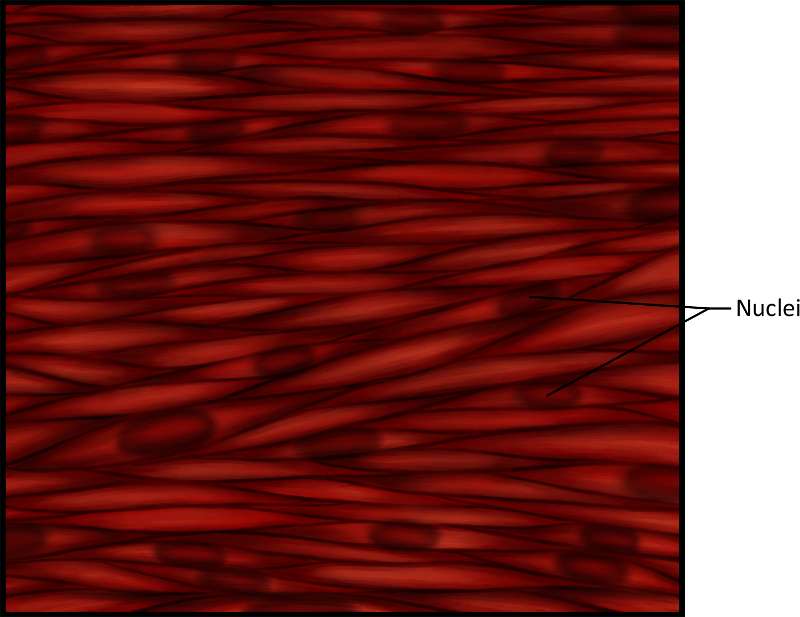
Figure 25. An illustration showing smooth muscle. The darkest stained cellular areas are the nuclei.
 |
|
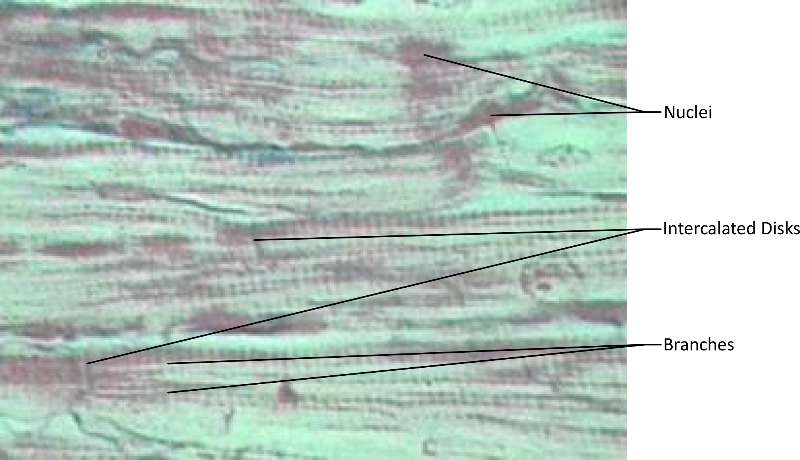
Figure 26. A micrograph (dyed purple for ease of visibilty). Notice the nuclei, branches and intercalated disks (junctions characteristic of cardiac muscle).
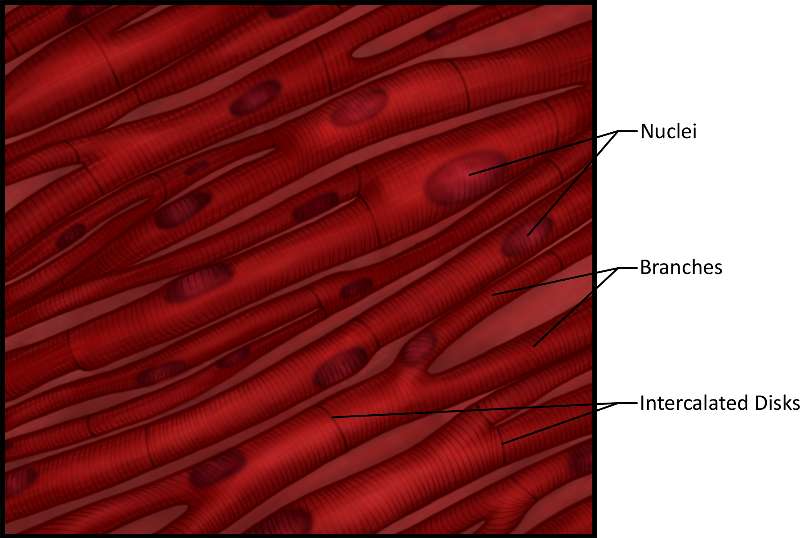
Figure 27. An illustration showing show smooth muscle. Note the nuclei, branches and intercalated disks (junctions characteristic of cardiac muscle).
Self-Check
| Click the card deck to view a card. Drag the card from the bottom to the correct category. | ||



